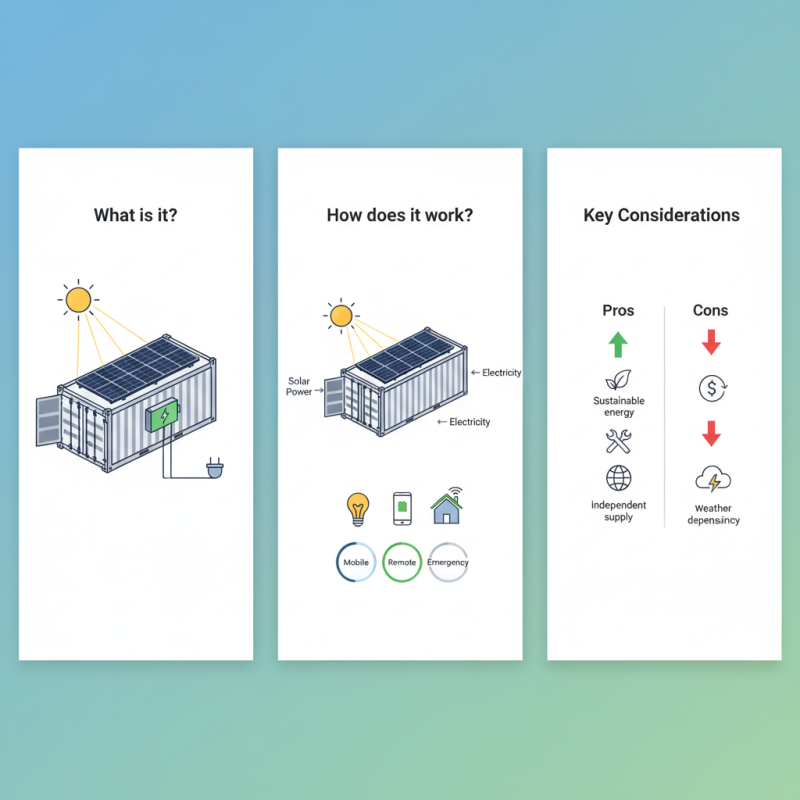
A solar container is an innovative energy solution designed for various applications. It harnesses solar power effectively, making it a valuable asset for many sectors. These containers are typically outfitted with solar panels and can convert sunlight into electricity. This feature allows for an independent power supply anywhere there is sunlight.
The versatility of solar containers is impressive. They can be used for mobile charging stations, remote power supply, or even disaster relief operations. With their compact design, they can be deployed quickly and easily. However, the initial investment can be a challenge for some users.
Many might question their long-term reliability. While they offer sustainable energy, factors like weather conditions can affect performance. Awareness of these limitations is important for potential users. Understanding these could lead to better, more informed decisions regarding solar container usage.
A solar container is a mobile energy solution that uses solar power. These innovative units are typically retrofitted shipping containers equipped with solar panels and energy storage systems. They can deliver power in remote locations, disaster zones, or during large events. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency, solar containers can reduce energy costs by up to 30% compared to traditional diesel generators.
Key features of solar containers include their portability and self-sufficiency. They can be transported easily to various sites. Many containers can generate 10-15 kW of power, suitable for small communities or temporary installations. However, factors like solar efficiency and local climate can affect performance. Some users report struggles with energy storage during cloudy days.
Despite their advantages, not every solar container is perfect. Maintenance can be more challenging in extreme weather. User experiences highlight the need for better efficiency in storage technology. Future improvements could address these issues. The focus on renewable energy is crucial, but real-world applications show we still have areas to improve.
This bar chart illustrates the distribution of solar container usage across various sectors including Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Agricultural. It highlights the growing trend of solar energy utilization in different fields.
Solar containers are innovative structures equipped with solar panels. They provide renewable energy solutions in various industries. One popular type is the solar shipping container. This container can be placed in remote areas, offering power without relying on traditional energy sources. It is commonly used on construction sites or for disaster relief efforts.
Another type is the solar container home. These residences not only contain solar panels but also can house essential amenities. Ideal for off-grid living, they offer sustainability. Various industries, such as agriculture, utilize these homes for seasonal workers. They help reduce the carbon footprint by promoting energy efficiency.
Tips: When considering solar containers, always assess location and weather patterns. Ensure adequate sunlight exposure for optimal energy capture. Evaluate your energy needs before purchasing. Solar containers can sometimes be costly, so planning is crucial. Consider how they can improve your environmental impact.
Solar containers are innovative solutions that utilize solar technology for various applications. These containers can be outfitted with solar panels, batteries, and other energy-efficient technologies. Their main purpose is to generate renewable energy in remote locations or during emergencies. Solar containers are portable, allowing easy deployment.
Efficiency metrics for solar containers are crucial for understanding their performance. According to industry reports, the average efficiency of solar panels installed on containers is around 15-20%. Some advanced setups can push this figure closer to 25%. Battery storage capacity often plays a key role too. Many containers are equipped with lithium-ion batteries, allowing for energy storage of about 10-20 kWh. This enables them to supply power during non-sunny days.
Tips: Ensure proper orientation of solar panels for maximum sunlight exposure. Regular maintenance checks can help optimize performance. It's essential to consider local weather patterns when deploying these containers. Using solar containers can lead to reliable energy supply, but their efficiency must be continuously monitored. Factors like dust accumulation and shading can impact overall performance. Test different setups to find what works best in your specific location.
Solar containers represent a flexible solution for renewable energy needs. They are mobile, self-sufficient units that harness solar power efficiently. These containers are equipped with solar panels, batteries, and sometimes inverters. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency, solar energy could provide up to 13% of the world's energy needs by 2030.
The benefits of solar containers extend beyond their portability. They reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprints. A study by the U.S. Department of Energy reveals that deploying solar containers can lower energy costs by up to 30%. This makes them attractive for various applications, from temporary power on construction sites to energy supply in remote areas.
However, challenges exist. Not all locations receive adequate sunlight year-round. This can impact their efficiency and reliability. Additionally, the initial cost may deter some users. Thoughtful consideration and careful planning are essential to maximize their potential. They are not a one-size-fits-all solution, highlighting the need for ongoing assessment in energy strategies.
Solar containers are innovative solutions to energy needs in remote areas. They provide clean, renewable energy in a compact, mobile format. Case studies around the world showcase their successful implementation.
In Kenya, solar containers are used in rural communities. They serve as mini power stations, supporting local businesses and schools. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency, access to renewable energy can increase local GDP by up to 5%. In some cases, these containers have doubled the energy access rates, significantly transforming daily life.
Another example is in Puerto Rico, post-hurricane recovery efforts utilized solar containers for temporary relief. Data from the World Bank highlights that restoring energy services quickly can reduce recovery time by 50%. However, challenges remain in integrating these systems fully into existing infrastructures. Many projects often struggled with local regulations or community engagement. The potential is immense, but it requires reflection and adaptation to local contexts.